Information Details
Misconceptions in Handling High-Temperature Fan Failures
Release time:
2022-04-11 10:23
Myth 1
The assembly gap of the high-temperature fan bearing outer ring is too large, resulting in the phenomenon of 'running ring'.
During the maintenance of the hot air fan, traces of relative sliding friction between the bearing outer ring and the bearing seat are often found. In severe cases, obvious steps are worn out on the cover of the bearing seat, and slight burning phenomena appear on the bearing outer ring, commonly referred to as 'bearing running ring'.
In fact, this 'bearing running ring' phenomenon often occurs during the operation of high-temperature fans. This is because the main shaft of the fan experiences thermal expansion during operation, and the bearing installation method is 'one end fixed, one end movable', resulting in a clearance fit between the bearing outer ring and the bearing seat hole. During operation, the non-locating end bearing moves axially with the expansion of the main shaft, and a certain degree of relative sliding between the bearing outer ring and the inner ring of the bearing seat driven by the rolling balls is permissible. When this situation occurs, it should not be simply assumed that 'bearing running ring' is causing the bearing to be pressed tightly, leading to accidents.
Myth 2
High fan vibration - rotor 'imbalance'.
As mentioned earlier, there are many reasons for high fan vibration, and rotor imbalance is just one of them. Many faults exhibit characteristics in spectrum analysis that are basically consistent with imbalance, but if not carefully checked and only eliminated through on-site dynamic balancing, it may reduce the vibration value but does not solve the fundamental problem. Sometimes it can even lead to a vicious cycle, such as dust accumulation on blades and cracking of interlayer welds; additionally, there are some faults whose spectrum characteristics are very similar to imbalance but are not actually imbalanced and cannot eliminate vibration through dynamic balancing, such as rotor bending and loose connections in the impeller.
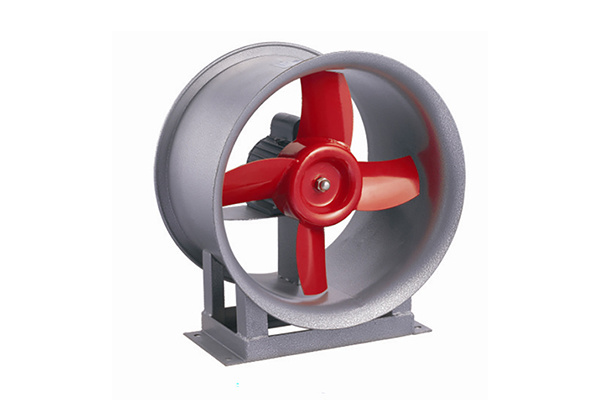
High temperature fan
RELATED INFORMATION